Hussein, January 2006
Introduction
Method
Primary fetal and adult fibroblasts were plated at a concentration of 1×105 cells/ml and grown on non-adherent plates in serum-free media at 37°C with concentrations of either 0, 1 or 5mg/ml AAGP®, with 10nM Coenzyme Q10. To test the affects of these two molecules on oxidative stress the cells were either exposed to 1mM hydrogen peroxide or UVC (256nm) rays for 3 hours. Cell counts were taken at various time points using Trypan blue and two counts were performed per sample to calculate the percentage viability (from 0 hours) of the cell sample.
Results
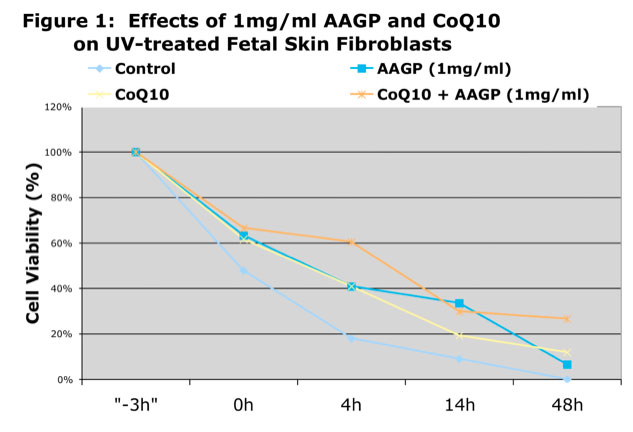
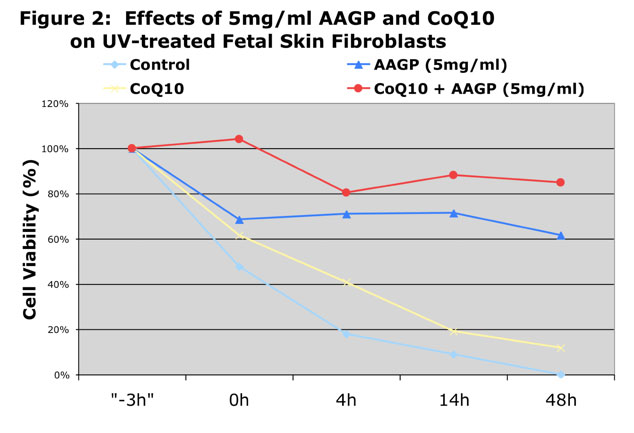
As can be seen from the graphs AAGP® and Coenzyme Q10 together provide more protection against UV and hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative stress than either one alone. These results demonstrate that combining AAGP® with CoQ10 had an additive effect. AAGP® synergies with CoQ10 to obtain increased cellular protection from UV or hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative stress.
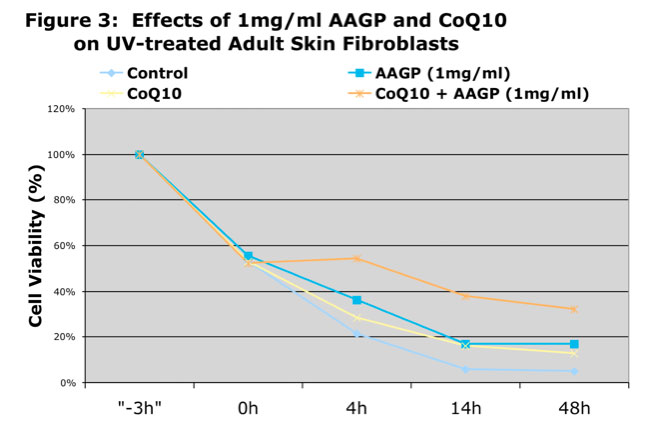
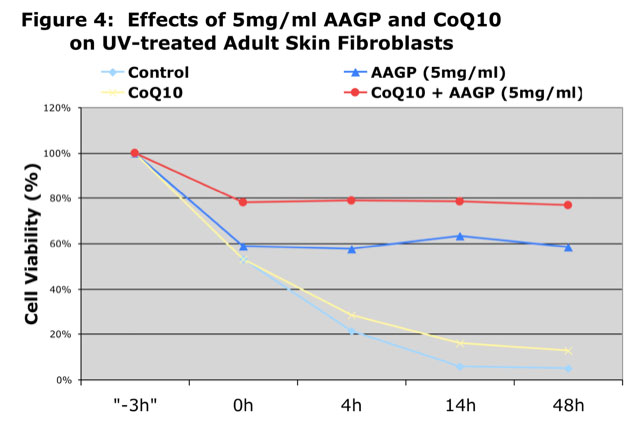
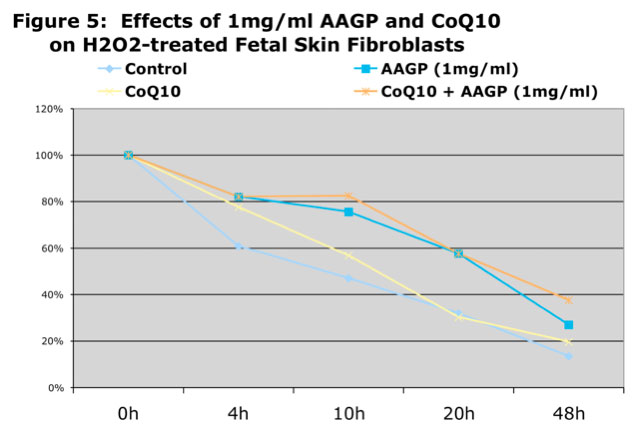
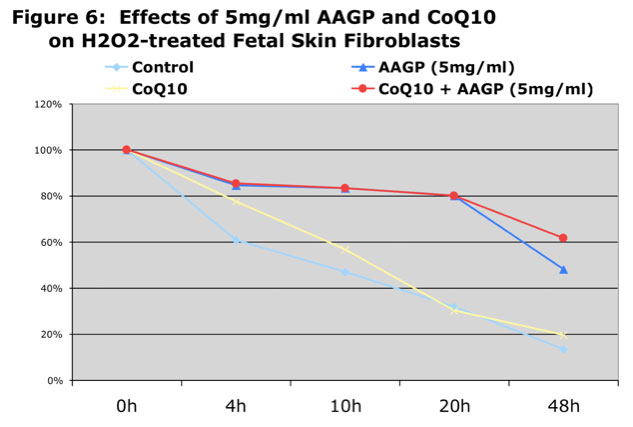
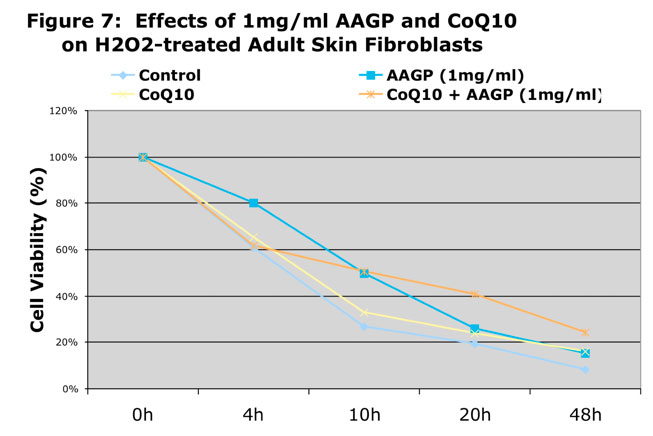
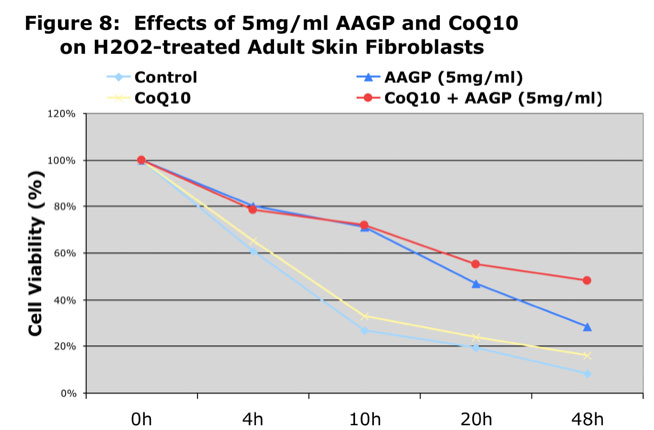
Conclusion
CoQ10 is a potent antioxidant found in the cells of the body which is now being added to some skin care products as an anti-aging substance and to prevent oxidative damage caused by environmental stresses. The additive effect of AAGP® and CoQ10 suggest AAGP® doesn’t have the same mechanism of action as CoQ10, which basically acts as a free radical scavenger.
One possible mechanism is that AAGP® alters the extracellular pH and in turn helps the cells to cope with stressful environments. In our previous experiments, we showed that AAGP® changes the pH to a more acidic pH, but in the absence of AAGP®, simply changing the pH was not enough to promote cell survival to the same extent, suggesting that pH change is not the only way AAGP® could protect cells. Another possibility, which is affected by both pH alteration and Anti-freeze proteins, is control of Ca+ influx; Ca+ accumulation is detrimental to cells and organs, and both pH change and anti-freeze proteins have been shown to inhibit this event. More future experiments will need to be conducted to address the mechanism of action of AAGP®.